Starbucks
Malaysia is a joint venture between Starbucks Coffee Company and Berjaya Group
Berhad. In 1998, Starbucks has entered Malaysian market with the first store at
KL Plaza in Kuala Lumpur (Market Watch, 2013) and it is operated by Berjaya
Starbucks Coffee Company Sdn. Bhd.. In January 2012, Starbucks were expended in
whole Malaysia with more than 140 stores in the country (Starbucks Coffee
Company, 2013). Starbucks is well known in the coffee industry. Starbucks
roasts and sells high quality of Arabica coffees and coffee drinks in their
outlets (Market Watch, 2013). Besides that, Starbucks also provide food such as
sandwich, cakes, and bread in their outlets.
In
Malaysia, Starbucks’s coffee is a luxury good so it would have elastic of
demand. When Starbucks’s coffee is a luxury good, consumer is very sensitive to
the price change. The consumer demand will drop drastically when the price of
the Starbucks coffee rises because consumer would consume lesser than before or
switch to a less costly alternatives (Sloman, Wride, and Garratt, 2012). When
the consumer consume lesser, the total consumer expenditure will decrease. Thus,
the total revenue receive by Starbucks will also be decreased. Graph 1 below
shows that a small change in price will have a huge change in the quantity (Sparknotes.com,
2013).
Graph 1
Besides that, there
are several determinants that cause the shifts of the demand curve. First of
all, it is the price of related goods. When the price of the substitute such as
tea is increase, the demand for Starbucks coffee will also increase. Moreover,
when the price of the complement such as milk is increase, the demand for
Starbucks coffee will decrease. The next determinant is the income. When the
income is increase, the demand of the luxury goods will increase and the demand
for normal good will decrease. For example, the demand for the Starbucks coffee
increases whereas the demand for McDonald’s coffee will decrease when there is
an increase in the income. Besides that, the expected future price is also one
of the determinants of demand. When the price of Starbucks coffee is expected
to be rise in the future, the current demand for the Starbucks coffee will
increase.
On the other hand, Starbucks are
willing to supply more coffee because the price of the coffee is relatively
high and they are able to cover their marginal cost of production (Sloman, Wride,
and Garratt, 2012). There are several determinants that cause the shifts of the
supply curve. First of all, it is the prices of factors of production. The
suppliers are not willing to supply more when the price of a factor of
production such as the farming cost for the coffee bean increased. Thus, the
supply curve will shifts to the left. The next determinant for supply is technology.
The brewing system that used in Starbucks could allow them to produce the
coffee within minutes. When the cost of production of Starbucks coffee is low,
they are willing to supply more. Therefore, the supply curve will shift to the
right. Moreover, the state of nature is also one of the determinants for
supply. For example, the storm in Colombia has cut down the production of
coffee bean to 10% in year 2010 (Walsh, 2011). When the supply is decrease, the
supply curve will shift to the left.
There are three
factors that influence the price elasticity of demand. The first factor is the
closeness of substitutes. When there is more substitutes are available in the
market, the demands for the Starbucks coffee will more elastic (Sloman, Wride, and
Garratt, 2012). For example, when the price of a cup of Starbucks coffee rose
from RM13 to RM14, consumer would start to a buy a cup of tea instead of coffee.
This indicates that Starbucks coffee is very elastic. On the other hand, if the
consumers are not willing to giving up the Starbucks coffee even the price is
very high; this indicates that Starbucks coffee is inelastic because there is
lesser substitute in the market.
The next factor that influences the
price elasticity of demand is the amount of income spent on the good. The
elasticity of demand of the Starbucks coffee is depend on the income that
consumer are willing to pay. When the income of consumers is increase, consumer
is more willing to pay for a cup of Starbucks coffee. For example, luxury good
like Starbucks coffee will become a normal good to some people because their
income allow them to spend more. However, when the income of consumer is not
increase, consumer is not willing to pay for a cup of Starbucks coffee. Hence,
the Starbucks coffee is very elastic.
The last factor that influences the
price elasticity of demand is the time. The longer the time, the more time you
can find substitutes. Thus, the demand for the Starbucks coffee is more
elastic. For example, caffeine addicted might be switch to tea when the time
given for them is long enough.
Starbucks
Malaysia is in a monopolistic competitive market structure. Monopolistic
competition can be defined as many firms are competing in the market but they
have some power to decide on the price (Sloman, Wride, and Garratt, 2012). Starbucks
are price maker so the demand curve faced by the firm is downward sloping. Coffee
is a homogeneous product but Starbucks has successfully differentiated their
product from their competitors with the brand, quality and taste. Therefore, Starbucks
are able to control its price.
In the short run, Starbucks
may earn supernormal profits because they are facing less competitors and their
product are differentiated from their competitors such as Coffee Bean and Tea
Leaf and San Francisco Coffee. When the marginal cost is equal to the marginal
revenue, Starbucks could maximize their profit (Sloman, Wride, and Garratt, 2012).
When Starbucks produce high quality of coffee, consumers are willing to pay at
a higher price because the consumption for coffee drinkers is increasing from Brazil
to Asia (Walsh, H, 2011). Therefore, Starbucks are able to earn supernormal
profits in short run.
In the long run, Starbucks will have
zero economic profit because there will be new firms enter in the market and some
of their customer may switch to other brands of coffee. For example, McDonald
has introduced a relatively cheaper coffee drinks compared to Starbucks which
has been proved popular (Miller, 2009). Therefore, it causes the demand for
Starbucks decreases. When the firm is in equilibrium, the demand curve which is
also the average revenue curve is tangential to the average cost curve. Graph 2
below shows the equilibrium short run and the long run under monopolistic
competitive (Bized.co.uk, 2001).
Graph 2
In Malaysia,
there is a price ceiling for the coffee industry. Price ceiling is a regulation
that set by the government which states that when the price charge higher than the
price set by the government it is considered illegal. Under Competition Act
2010, coffee shops are allowed to charge different prices on their products but
the price charge must be reasonable (Borneo Post Online, 2013).
Furthermore, government in Malaysia
has imposed indirect tax to certain prescribed goods and services such as food,
drinks and tobacco (NBC Group, 2013). The rate of the service tax is 6% which
will be pay by the consumer for every purchased. Hence, the price of Starbucks coffee
will increase by 6% for every purchased. When the consumers pay all of the tax,
the firm is in the perfectly elastic supply.
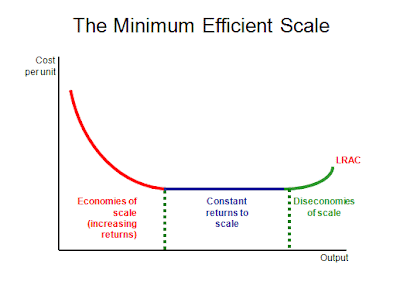
In the long run production,
Starbucks may experiences economies of scale as well as diseconomies of scale. When
Starbucks is in the economies of scale, the long run average cost is decrease
because the coffee that they produce is increasing. However, when Starbucks is
in the diseconomies of scale, the long run average cost is started to increase
because the coffee that they produce is increase. For example, the brewing
machines that used in Starbucks allow them to produce many cups of coffee
within minutes. Therefore, their long run average cost is decrease because they
are able to earn profit at this point and so Starbucks is in economies of
scale. Before the diseconomies of scale occur, constant return to scale will be
occurred. In constant return to scale, the long run average cost is kept
constant when Starbucks are able to increase their production. However, the
brewing machines in Starbucks need to be repair or do maintenance due to long
period of usage. So the long run average cost is started to increase and yet
Starbucks still increasing their production. At this point, Starbucks is in diseconomies
of scale. Graph 3 below shows the long run average cost curve for economies,
constant, and diseconomies of scale (Riley, 2012).
Graph 3
In
conclusion, Starbucks Malaysia is a monopolistic competitive and they are price
maker in the market. They usually set a higher price compared to their
competitor because their product is differentiated. They can gain loyal
customer form their product differentiation. Loyal consumers are willing to pay
at a higher price because the quality of coffee that Starbucks produce meets
their preferences.
(1518 words)
By Chai Ching Wan (0311880)
Reference
Bized.co.uk.
(2001) Monopolistic Competition -
Short Run to Long Run. [online] Available at:
http://www.bized.co.uk/reference/diagrams/Monopolistic-Competition---Short-Run-to-Long-Run
[Accessed: 23 Oct 2013].
Borneo Post Online (2013) ‘Have a cuppa
with us before upping prices’. [online] Available at: http://www.theborneopost.com/2013/10/20/have-a-cuppa-with-us-before-upping-prices/
[Accessed: 23 Oct 2013].
Market Watch (2013) Starbucks Announces the Opening of 100 New Stores in Malaysia over the
Next Four Years. [online] Available at:
http://www.marketwatch.com/story/starbucks-announces-the-opening-of-100-new-stores-in-malaysia-over-the-next-four-years-2013-06-26
[Accessed: 20 Oct 2013].
Miller, C (2009) Will the Hard-Core
Starbucks Customer Pay More? The Chain Plans to Find Out. [online] Available
at: http://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/21/business/21sbux.html?_r=0
[Accessed:
22 Oct 2013].
NBC Group (2013) Service Tax in
Malaysia. [online] Available at: http://www.nbc.com.my/service-tax-in-malaysia.html
[Accessed: 23 Oct 2013].
Riley, G (2012) Unit 3 Micro: Revision on Scale Economies and MES. [online]
Available at:
http://www.tutor2u.net/blog/index.php/economics/comments/unit-3-micro-revision-on-scale-economies-and-mes
[Accessed: 24 Oct 2013].
Sloman, J., Wride, A. and
Garratt, D. (2012) Economics. Eighth Edition. Pearson.
Sparknotes.com (2013) SparkNotes: Elasticity: Elasticity.
[online] Available at:
http://www.sparknotes.com/economics/micro/elasticity/section1.rhtml [Accessed:
21 Oct 2013].
Starbucks Coffee Company (2013) Starbucks Malaysia. [online]
Available at: http://www.starbucks.com.my/about-us/starbucks-malaysia
[Accessed: 20 Oct 2013].
Walsh, H (2011) Starbucks Drinkers Won’t Get Break as Colombia Supply Drops.
[online] Available at:
http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2011-05-26/coffee-drinkers-won-t-get-price-break-as-colombia-supply-slumps.html
[Accessed: 24 Oct 2013].


Good sharing, Starbucks now offers its premier coffee brand Starbucks Reserve to Malaysians, further strengthening its hold as the coffee franchise powerhouse and authority in the country. Head to Starbucks Reserve The Gardens shopping mall today to heighten your senses and take pleasure in a cup of good coffee made by the best, see detail at:
ReplyDeletehttp://kidbuxblog.com/starbucks-opens-its-first-premier-reserve-store-in-malaysia/
Best Regards,
Your favorite Split Queen Box Springs or split queen box spring mattress selection.
Betway Login Casino - JT Hub
ReplyDeleteYou can use 강릉 출장샵 this Betway login 제주 출장마사지 casino page to create a casino account 경산 출장마사지 or login in Betway Casino. · 경산 출장마사지 Login to Betway Login. · Create a new account · Click 김포 출장마사지 Login